Solutions for the transmission of network CCTV systems over long distances in a Zone 1 environment.

Huan He
October 14, 2024
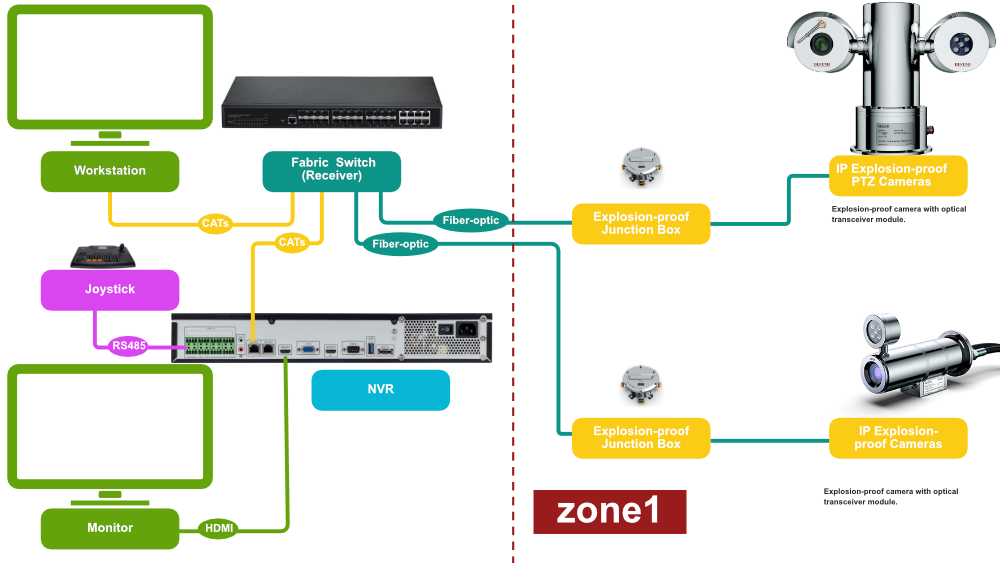
In a Zone 1 environment, connecting explosion proof cameras located more than 200 meters away from the Network Video Recorder (NVR) requires special design considerations. Since standard Ethernet cabling (e.g., Cat5e/Cat6) is limited to 100 meters, you will need appropriate relay and transmission equipment while ensuring safety and compliance with ATEX or IECEx standards for hazardous environments.
-
1. Use Fiber Optic Cabling
Fiber Optic Cables are ideal for long-distance transmission in hazardous environments, as they can transmit data over several kilometers without signal degradation. They are also immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and do not generate sparks, making them safer for use in explosive environments.
Single-mode fiber is often used for long distances, such as those beyond 200 meters, as it can easily cover distances up to 10 kilometers or more.
Multi-mode fiber could also be used for distances of a few hundred meters , but is less efficient over very long distances.
-
Required components
-
Explosion proof camera (Zone 1)
Install an explosion-proof camera with a fiber optic interface, or connect the camera to a media converter that converts Ethernet signals to fiber optics.
-
Media Converter
The fibre optic media converter used must be installed in an explosion-proof box or the Ethernet output of the Explosion proof camera must be converted to a fibre optic signal.
For cameras with Power over Ethernet (PoE), use PoE media converters that split power and data, or run a separate power line if PoE is not supported over fiber.
-
Fiber Optic Cable
Run a single-mode fiber optic cable from the camera to a safe area outside Zone 1 or to the NVR directly (if the distance allows).
-
At the NVR End
At the NVR location, use another media converter to convert the fiber signal back to Ethernet for connection to the NVR.
-
-
-
2. PoE Extenders or Repeaters (for Copper Ethernet)
If fiber optics is not feasible and you prefer to use copper Ethernet (Cat5e/Cat6), you will need PoE extenders or repeaters to bridge the 200-meter distance, used every 100 meters. However, these devices must be used outside the hazardous area or housed in explosion-proof enclosures when used within Zone 1.
-
Required components
-
Explosion proof camera (Zone 1)
Use an explosion-proof PoE camera.
-
PoE Extender
Install a PoE extender or Ethernet switch with PoE support every 100 meters. Since PoE over copper Ethernet is limited to 100 meters, using PoE extenders in between will allow you to reach the 200 meters distance.
Ensure the PoE extender or switch is either located outside Zone 1 or housed in an ATEX-certified explosion-proof enclosure.
-
NVR Connection
At the NVR end, connect the Ethernet cable from the last PoE extender or switch directly to the NVR.
-
-
-
3. Use Wireless Bridge (if cabling is impractical)
If running cables is not practical due to site conditions (e.g., in large industrial plants or offshore platforms), a wireless bridge may be used. The wireless bridge components must also be explosion-proof or located outside Zone 1.
-
Required components
-
Explosion proof camera (Zone 1)
Install an explosion-proof IP camera.
-
Explosion-Proof Wireless Bridger
Set up an explosion-proof wireless bridge system in the hazardous area. This typically includes a transmitter near the camera and a receiver outside the hazardous zone.
-
NVR Connection
The wireless receiver is connected via Ethernet to the NVR. Ensure the wireless signal covers the 200-meter distance (wireless bridges can cover several kilometers with line-of-sight).
-
-